Hi Friends .
Like Shear and Comments these Post.
* ओम का नियम *
ओम का नियम और प्रतिरोध: -
ओम का नियम बताता है कि दो बिंदुओं के बीच वोल्टेज या संभावित अंतर वैध रूप से प्रतिरोध के माध्यम से गुजरने वाली वर्तमान या बिजली के सापेक्ष है, और सीधे सर्किट के प्रतिरोध के अनुरूप है। ओम के नियम के लिए समीकरण (V = IR) है। वर्तमान, वोल्टेज और संबंध के बीच इस संबंध की खोज जर्मन वैज्ञानिक जॉर्ज साइमन ओह्म ने की थी। आइए हम ओम कानून, प्रतिरोध और इसके अनुप्रयोगों से परिचित हों।
ओम का नियम परिभाषा: -
बिजली के अधिकांश बुनियादी घटक वोल्टेज, करंट और प्रतिरोध हैं। ओम का नियम इन तीन राशियों के बीच एक सरल संबंध दर्शाता है। ओम का नियम बताता है कि दो बिंदुओं के बीच एक चालक के माध्यम से धारा सीधे दो बिंदुओं पर वोल्टेज के अनुरूप होती है।
ओम का नियम :-
ओम का नियम सूत्र: -
वोल्टेज = करंट × प्रतिरोध
वी = आई × आर ( V=IR)
वी = वोल्टेज, मैं = वर्तमान और आर = प्रतिरोध
प्रतिरोध की SI इकाई ओम है और इसे is द्वारा दर्शाया गया है
यह कानून बिजली के सबसे बुनियादी कानूनों में से एक है। यह विद्युत सर्किट के एक घटक के बल, उत्पादकता, वर्तमान, वोल्टेज और प्रतिरोध की गणना करने में मदद करता है।
ओम के नियम के अनुप्रयोग: -
ओम का नियम हमें वोल्टेज, करंट या प्रतिबाधा या एक सीधे विद्युत परिपथ के प्रतिरोध को तय करने में हमारी मदद करता है जब अन्य दो मात्राओं को हम जानते हैं। यह पावर काउंट को भी सरल बनाता है।
हम वर्तमान-वोल्टेज संबंध कैसे स्थापित करेंगे?
इसलिए वर्तमान-वोल्टेज संबंध स्थापित करने के लिए, अनुपात V / I एक दिए गए प्रतिरोध के लिए स्थिर रहता है, फलस्वरूप संभावित विपरीत (V) और वर्तमान (I) के बीच का एक आरेख सीधी रेखा होना चाहिए।
हम प्रतिरोध के अस्पष्ट मूल्यों का पता कैसे लगाएंगे?
यह निरंतर अनुपात है जो प्रतिरोध के अस्पष्ट मूल्यों को देता है,
समान क्रॉस-सेक्शन के एक तार के लिए, प्रतिरोध लंबाई एल और क्रॉस-सेक्शन ए के क्षेत्र पर निर्भर करता है। यह कंडक्टर के तापमान पर भी निर्भर करता है। दिए गए तापमान पर प्रतिरोध,
जहां ρ विशिष्ट प्रतिरोध या प्रतिरोधकता है और तार की सामग्री की विशेषता है। तार की सामग्री का विशिष्ट प्रतिरोध या प्रतिरोधकता है,
बंद मौका पर कि 'आर' तार की त्रिज्या है, उस बिंदु पर क्रॉस-अनुभागीय क्षेत्र, ए ='r =। उस बिंदु पर तार की सामग्री का विशिष्ट प्रतिरोध या प्रतिरोधकता है,
ओम कानून की सीमाएं: -
ओम का नियम एकतरफा नेटवर्क के लिए उचित नहीं है। एक तरफा नेटवर्क धारा को एक तरह से प्रवाहित करने की अनुमति देता है। इस तरह के सिस्टम में डायोड, ट्रांजिस्टर और आगे जैसे तत्व होते हैं।
ओम का नियम गैर-प्रत्यक्ष तत्वों के लिए भी प्रासंगिक नहीं है। गैर-प्रत्यक्ष तत्व वे होते हैं जिनके पास लागू वोल्टेज के अनुरूप वर्तमान ठीक नहीं होता है, जिसका अर्थ है कि वोल्टेज और वर्तमान के विभिन्न मूल्यों के लिए उन तत्वों के प्रतिरोध का अनुमान बदल जाता है। गैर - सीधे तत्वों के उदाहरण थायरिस्टर हैं।
प्रतिरोधों: -
रोकनेवाला
प्रतिरोध विद्युत सर्किट के महत्वपूर्ण ब्लॉकों में से एक है। वे मिट्टी या कार्बन के मिश्रण से युक्त होते हैं, इसलिए वे स्वीकार्य कंडक्टर और साथ ही महान इन्सुलेटर भी होते हैं। अधिकांश प्रतिरोधों में चार छायांकन बैंड होते हैं। पहला और दूसरा बैंड क्रमशः मूल्य के पहले और दूसरे अंक को उजागर करता है। तीसरे बैंड का उपयोग मूल्य अंकों की नकल करने के लिए किया जाता है और चौथा बैंड हमें प्रतिरोध बताता है। इस घटना में कि कोई चौथा बैंड नहीं है, यह माना जाता है कि लचीलापन प्लस या माइनस 20% है।
श्रृंखला में प्रतिरोध: -
एक श्रृंखला और बड़े साधन एक पंक्ति के साथ, या उत्तराधिकार में, या एक अनुरोध में जुड़े हुए हैं। इलेक्ट्रॉनिक्स में, श्रृंखला प्रतिरोध का मतलब है कि प्रतिरोधक एक के बाद एक जुड़े हुए हैं और धारा के माध्यम से प्रवाह के लिए धारा के लिए एक ही रास्ता है।
स्रोत: स्पार्कफुन
श्रृंखला सर्किट के कानून
विलक्षण प्रतिरोध का मतलब है कि सभी सर्किट प्रतिरोध
सर्किट के माध्यम से वर्तमान प्रत्येक बिंदु पर समान है।
पूरे सर्किट में विलक्षण वोल्टेज निरपेक्ष वोल्टेज का संकेत देते हैं।
बराबर में प्रतिरोध: -
बराबर सर्किट को सॉर्ट करने के कई तरीके हैं। डाउन टू अर्थ की दुनिया में, अधिकांश वायरिंग समान रूप से की जाती है ताकि सिस्टम के किसी एक टुकड़े को वोल्टेज उसी तरह का हो जैसे किसी अन्य टुकड़े को आपूर्ति की गई वोल्टेज।
समानांतर सर्किट के नियम: -
सभी व्यक्तिगत प्रतिरोधों के पारस्परिक सभी सर्किट प्रतिरोध के बराबर इंगित करते हैं।
1 / RT = 1 / R1 + 1 / R2 + 1 / R3…
सर्किट के माध्यम से वोल्टेज प्रत्येक बिंदु पर समान है।
पूरे सर्किट में सिंगुलर करंट ड्रॉ का मतलब ऑल आउट करंट ड्रॉ है।
* ओम का नियम *
ओम का नियम और प्रतिरोध: -
ओम का नियम बताता है कि दो बिंदुओं के बीच वोल्टेज या संभावित अंतर वैध रूप से प्रतिरोध के माध्यम से गुजरने वाली वर्तमान या बिजली के सापेक्ष है, और सीधे सर्किट के प्रतिरोध के अनुरूप है। ओम के नियम के लिए समीकरण (V = IR) है। वर्तमान, वोल्टेज और संबंध के बीच इस संबंध की खोज जर्मन वैज्ञानिक जॉर्ज साइमन ओह्म ने की थी। आइए हम ओम कानून, प्रतिरोध और इसके अनुप्रयोगों से परिचित हों।
ओम का नियम परिभाषा: -
बिजली के अधिकांश बुनियादी घटक वोल्टेज, करंट और प्रतिरोध हैं। ओम का नियम इन तीन राशियों के बीच एक सरल संबंध दर्शाता है। ओम का नियम बताता है कि दो बिंदुओं के बीच एक चालक के माध्यम से धारा सीधे दो बिंदुओं पर वोल्टेज के अनुरूप होती है।
ओम का नियम :-
ओम का नियम सूत्र: -
वोल्टेज = करंट × प्रतिरोध
वी = आई × आर ( V=IR)
वी = वोल्टेज, मैं = वर्तमान और आर = प्रतिरोध
प्रतिरोध की SI इकाई ओम है और इसे is द्वारा दर्शाया गया है
यह कानून बिजली के सबसे बुनियादी कानूनों में से एक है। यह विद्युत सर्किट के एक घटक के बल, उत्पादकता, वर्तमान, वोल्टेज और प्रतिरोध की गणना करने में मदद करता है।
ओम के नियम के अनुप्रयोग: -
ओम का नियम हमें वोल्टेज, करंट या प्रतिबाधा या एक सीधे विद्युत परिपथ के प्रतिरोध को तय करने में हमारी मदद करता है जब अन्य दो मात्राओं को हम जानते हैं। यह पावर काउंट को भी सरल बनाता है।
हम वर्तमान-वोल्टेज संबंध कैसे स्थापित करेंगे?
इसलिए वर्तमान-वोल्टेज संबंध स्थापित करने के लिए, अनुपात V / I एक दिए गए प्रतिरोध के लिए स्थिर रहता है, फलस्वरूप संभावित विपरीत (V) और वर्तमान (I) के बीच का एक आरेख सीधी रेखा होना चाहिए।
हम प्रतिरोध के अस्पष्ट मूल्यों का पता कैसे लगाएंगे?
यह निरंतर अनुपात है जो प्रतिरोध के अस्पष्ट मूल्यों को देता है,
समान क्रॉस-सेक्शन के एक तार के लिए, प्रतिरोध लंबाई एल और क्रॉस-सेक्शन ए के क्षेत्र पर निर्भर करता है। यह कंडक्टर के तापमान पर भी निर्भर करता है। दिए गए तापमान पर प्रतिरोध,
जहां ρ विशिष्ट प्रतिरोध या प्रतिरोधकता है और तार की सामग्री की विशेषता है। तार की सामग्री का विशिष्ट प्रतिरोध या प्रतिरोधकता है,
बंद मौका पर कि 'आर' तार की त्रिज्या है, उस बिंदु पर क्रॉस-अनुभागीय क्षेत्र, ए ='r =। उस बिंदु पर तार की सामग्री का विशिष्ट प्रतिरोध या प्रतिरोधकता है,
ओम कानून की सीमाएं: -
ओम का नियम एकतरफा नेटवर्क के लिए उचित नहीं है। एक तरफा नेटवर्क धारा को एक तरह से प्रवाहित करने की अनुमति देता है। इस तरह के सिस्टम में डायोड, ट्रांजिस्टर और आगे जैसे तत्व होते हैं।
ओम का नियम गैर-प्रत्यक्ष तत्वों के लिए भी प्रासंगिक नहीं है। गैर-प्रत्यक्ष तत्व वे होते हैं जिनके पास लागू वोल्टेज के अनुरूप वर्तमान ठीक नहीं होता है, जिसका अर्थ है कि वोल्टेज और वर्तमान के विभिन्न मूल्यों के लिए उन तत्वों के प्रतिरोध का अनुमान बदल जाता है। गैर - सीधे तत्वों के उदाहरण थायरिस्टर हैं।
प्रतिरोधों: -
रोकनेवाला
प्रतिरोध विद्युत सर्किट के महत्वपूर्ण ब्लॉकों में से एक है। वे मिट्टी या कार्बन के मिश्रण से युक्त होते हैं, इसलिए वे स्वीकार्य कंडक्टर और साथ ही महान इन्सुलेटर भी होते हैं। अधिकांश प्रतिरोधों में चार छायांकन बैंड होते हैं। पहला और दूसरा बैंड क्रमशः मूल्य के पहले और दूसरे अंक को उजागर करता है। तीसरे बैंड का उपयोग मूल्य अंकों की नकल करने के लिए किया जाता है और चौथा बैंड हमें प्रतिरोध बताता है। इस घटना में कि कोई चौथा बैंड नहीं है, यह माना जाता है कि लचीलापन प्लस या माइनस 20% है।
श्रृंखला में प्रतिरोध: -
एक श्रृंखला और बड़े साधन एक पंक्ति के साथ, या उत्तराधिकार में, या एक अनुरोध में जुड़े हुए हैं। इलेक्ट्रॉनिक्स में, श्रृंखला प्रतिरोध का मतलब है कि प्रतिरोधक एक के बाद एक जुड़े हुए हैं और धारा के माध्यम से प्रवाह के लिए धारा के लिए एक ही रास्ता है।
स्रोत: स्पार्कफुन
श्रृंखला सर्किट के कानून
विलक्षण प्रतिरोध का मतलब है कि सभी सर्किट प्रतिरोध
सर्किट के माध्यम से वर्तमान प्रत्येक बिंदु पर समान है।
पूरे सर्किट में विलक्षण वोल्टेज निरपेक्ष वोल्टेज का संकेत देते हैं।
बराबर में प्रतिरोध: -
बराबर सर्किट को सॉर्ट करने के कई तरीके हैं। डाउन टू अर्थ की दुनिया में, अधिकांश वायरिंग समान रूप से की जाती है ताकि सिस्टम के किसी एक टुकड़े को वोल्टेज उसी तरह का हो जैसे किसी अन्य टुकड़े को आपूर्ति की गई वोल्टेज।
समानांतर सर्किट के नियम: -
सभी व्यक्तिगत प्रतिरोधों के पारस्परिक सभी सर्किट प्रतिरोध के बराबर इंगित करते हैं।
1 / RT = 1 / R1 + 1 / R2 + 1 / R3…
सर्किट के माध्यम से वोल्टेज प्रत्येक बिंदु पर समान है।
पूरे सर्किट में सिंगुलर करंट ड्रॉ का मतलब ऑल आउट करंट ड्रॉ है।









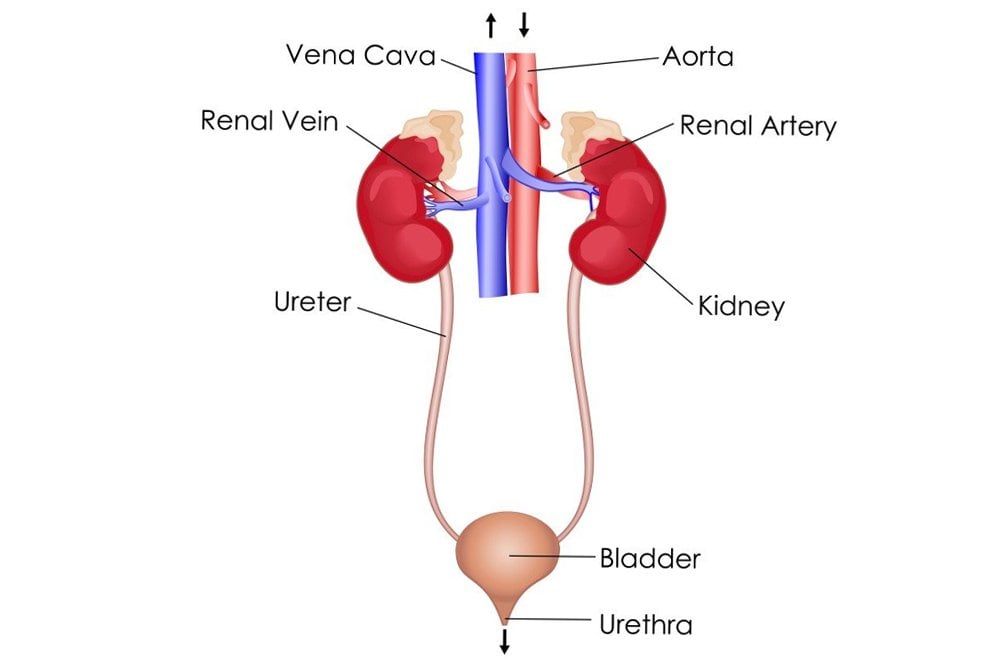





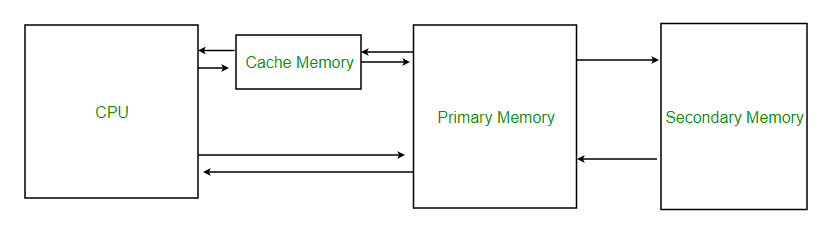
 Disk Caches :
Disk Caches :
