* Velocity / वेग *
वेग को गति और गति की दिशा के वेक्टर अनुमान के रूप में जाना जाता है।
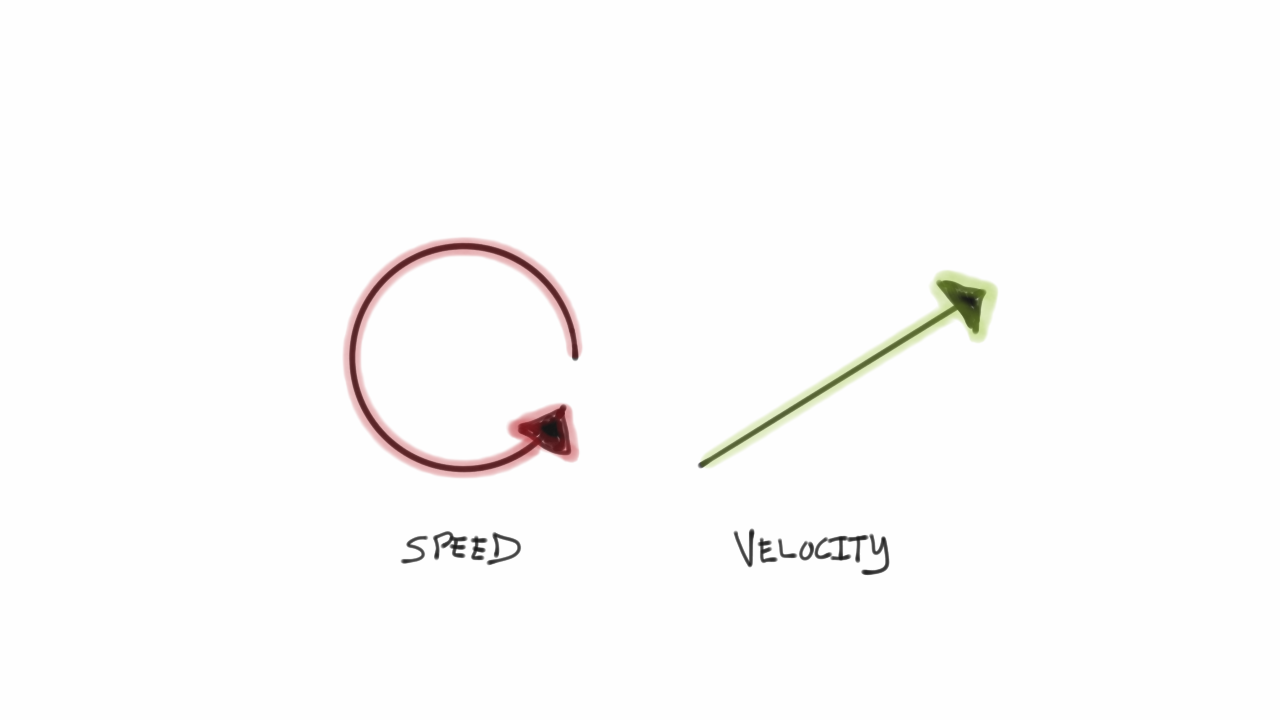
"वेग वह गति है जिस पर कुछ विशिष्ट दिशा में गति करता है, उदाहरण के लिए, एक महत्वपूर्ण सड़क पर उत्तर की ओर जाने वाले वाहन की गति, या एक रॉकेट गति के रूप में अंतरिक्ष में भेज देता है। वेग वेक्टर की स्केलर (सर्वोच्च मूल्य) की गति गति है। गणित के संदर्भ में, वेग समय के संबंध में स्थिति का मुख्य अधीनस्थ है।


वेग, परिभाषा के अनुसार, एक सदिश राशि है जो समय और दिशा के अनुसार दूरी दिखाती है। गति की तरह, इसकी इकाइयाँ लंबाई और समय होती हैं, हालांकि दिशा भी इसी तरह की स्थिति से जुड़ी होती है। दूरी के बजाय वेग कुछ समय बाद हटाने का अनुमान लगाता है।

आप एक सीधे सूत्र का उपयोग करके वेग का पता लगा सकते हैं जो उपयोग दर, दूरी और समय का उपयोग करता है।
वेग सूत्र - :सीधी रेखा में चलने वाली वस्तु के निरंतर वेग का पता लगाने के लिए सबसे प्रसिद्ध तरीका सूत्र के साथ है:
R =D / T
कहाँ पे
r= दर, या गति है (कभी-कभी वेग के रूप में v के रूप में इंगित की जाती है),
d= कितनी दूरी पर है,
t =विकास को पूरा करने में लगने वाला समय है
वेग की इकाइयाँ :-
वेग के लिए SI (विश्वव्यापी) इकाइयाँ m / s (मीटर हर सेकंड) हैं। किसी भी स्थिति में, प्रति समय दूरी की किसी भी इकाई में वेग का संचार किया जा सकता है। विभिन्न इकाइयाँ मील को हर घंटे (mph), किलोमीटर को हर घंटे (kph), और किलोमीटर को हर सेकंड (किमी / सेकंड) में शामिल करती हैं
Velocity is characterized as a vector estimation of the rate and direction of movement." velocity is the speed at which something moves in a specific direction", for example, the speed of a vehicle voyaging north on a significant road, or the speed a rocket goes as it dispatches into space. The scalar (supreme worth) extent of the velocity vector is the speed of the movement. In math terms, velocity is the main subordinate of situation concerning time.
Velocity, by definition, is a vector amount that shows distance per time and direction. Like speed, its units are length and time, however direction is likewise engaged with the condition. Velocity estimates removal after some time, instead of distance.
You can ascertain velocity by utilizing a straightforward formula that utilization's rate, distance, and time.
Velocity Formula
The most well-known approach to ascertain the consistent velocity of an item moving in a straight line is with the formula:
( r = d/t ) m/s
where
r= is the rate, or speed (sometimes indicated as v, for velocity) ,
d= is the distance moved ,
t =is the time it takes to finish the development .
Units of Velocity :-
The SI (worldwide) units for velocity are m/s (meters every second). In any case, velocity might be communicated in any units of distance per time. Different units incorporate miles every hour (mph), kilometers every hour (kph), and kilometers every second (km/s)
वेग को गति और गति की दिशा के वेक्टर अनुमान के रूप में जाना जाता है।
"वेग वह गति है जिस पर कुछ विशिष्ट दिशा में गति करता है, उदाहरण के लिए, एक महत्वपूर्ण सड़क पर उत्तर की ओर जाने वाले वाहन की गति, या एक रॉकेट गति के रूप में अंतरिक्ष में भेज देता है। वेग वेक्टर की स्केलर (सर्वोच्च मूल्य) की गति गति है। गणित के संदर्भ में, वेग समय के संबंध में स्थिति का मुख्य अधीनस्थ है।
वेग, परिभाषा के अनुसार, एक सदिश राशि है जो समय और दिशा के अनुसार दूरी दिखाती है। गति की तरह, इसकी इकाइयाँ लंबाई और समय होती हैं, हालांकि दिशा भी इसी तरह की स्थिति से जुड़ी होती है। दूरी के बजाय वेग कुछ समय बाद हटाने का अनुमान लगाता है।

आप एक सीधे सूत्र का उपयोग करके वेग का पता लगा सकते हैं जो उपयोग दर, दूरी और समय का उपयोग करता है।
वेग सूत्र - :सीधी रेखा में चलने वाली वस्तु के निरंतर वेग का पता लगाने के लिए सबसे प्रसिद्ध तरीका सूत्र के साथ है:
R =D / T
कहाँ पे
r= दर, या गति है (कभी-कभी वेग के रूप में v के रूप में इंगित की जाती है),
d= कितनी दूरी पर है,
t =विकास को पूरा करने में लगने वाला समय है
वेग की इकाइयाँ :-
वेग के लिए SI (विश्वव्यापी) इकाइयाँ m / s (मीटर हर सेकंड) हैं। किसी भी स्थिति में, प्रति समय दूरी की किसी भी इकाई में वेग का संचार किया जा सकता है। विभिन्न इकाइयाँ मील को हर घंटे (mph), किलोमीटर को हर घंटे (kph), और किलोमीटर को हर सेकंड (किमी / सेकंड) में शामिल करती हैं
Velocity is characterized as a vector estimation of the rate and direction of movement." velocity is the speed at which something moves in a specific direction", for example, the speed of a vehicle voyaging north on a significant road, or the speed a rocket goes as it dispatches into space. The scalar (supreme worth) extent of the velocity vector is the speed of the movement. In math terms, velocity is the main subordinate of situation concerning time.
Velocity, by definition, is a vector amount that shows distance per time and direction. Like speed, its units are length and time, however direction is likewise engaged with the condition. Velocity estimates removal after some time, instead of distance.
You can ascertain velocity by utilizing a straightforward formula that utilization's rate, distance, and time.
Velocity Formula
The most well-known approach to ascertain the consistent velocity of an item moving in a straight line is with the formula:
( r = d/t ) m/s
where
r= is the rate, or speed (sometimes indicated as v, for velocity) ,
d= is the distance moved ,
t =is the time it takes to finish the development .
Units of Velocity :-
The SI (worldwide) units for velocity are m/s (meters every second). In any case, velocity might be communicated in any units of distance per time. Different units incorporate miles every hour (mph), kilometers every hour (kph), and kilometers every second (km/s)



No comments:
Post a Comment